HTML Exercises
1. Online Newspaper
Using HTML 5 only, create a prototype of an online newspaper:
- Throughout this exercise, do not worry about design. HTML is a markup language with pre-defined presentation semantics; the design is handled by CSS (more on this next week).
- For now, you can edit your HTML files locally.
- Validate and verify the result on the browser as you proceed.
Some tips and ideas:
- Use the site http://www.lipsum.com/ (or any LLM) if you need to generate example paragraphs.
- Use the site https://picsum.photos/ if you need some example photos.
Instructions:
- In this exercise, you will create the pages described in the following image:
- The main page represents the main page of the newspaper having a series of abbreviated news items.
- The news article page has one particular news item in its complete form. It also has comments written by the readers.
- The section page is very similar to the main page, but only has news about a particular topic (e.g., sports).
- For each page, create a new HTML file, open it with your favorite code editor, and add the following basic HTML code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Online Newspaper</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Open the main page in a web browser (the most straightforward way is to drag the file into a new tab).
Complete each page using the correct semantic elements.
- The header of each page should have:
- The name of the newspaper.
- A logo.
- The section's name (if it's a section page).
- Clicking any of these elements should take the user back to the main page.
- The menu should have links to each one of the section pages (e.g., sports, politics, and local)
- The links should be part of an unordered list.
- For now, all of those can point to section.html.
- Each article should have a title, some paragraphs, an image, and a footer.
- In the main and section pages, only a couple of paragraphs of each news item should be shown.
- The news article page should also have some comments. Each comment should have some text, a date/time, and the author's username. After the comments, include a form where users can add their own. The form should have a title, a username field, and a text field for the comment content.
- The footer should contain the date/time and the author's name. In the main and section pages, there should also be a "Read more" link that redirects the user to the news article page containing the complete news item.
- The footer of each page should have a Copyright Notice. Use a character entity for the © symbol.
- The header of each page should have:
Don't forget to validate the pages when you're done.
What did I learn:
- The basics of HTML documents.
- The usage of section elements.
- How to validate an HTML page.
- HTML is not for design!
2. Complex Table
Using HTML 5 only, create a document representing the following table.
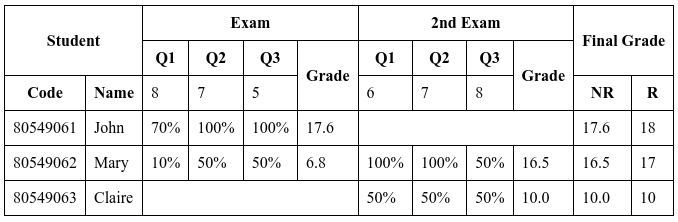
As we still don't know CSS, let's use the attribute border= "1" to visualize the result better:
<table border="1">
<tr>...</tr>
...
</table>
Or, if you want to be fancy, you can use CSS (spoiler alert). Just add this to the document's head element:
<style>
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th, td {
border:1px solid;
padding: 0.5em;
}
</style>
Tip: The easiest way to implement complex tables in HTML is to think about the table row by row. This table has 6 rows.
When you are finished:
- Validate the HTML code.
- Include an HTML 5 badge on the webpage.
- Revalidate the document.
What did I learn:
- How to create a complex HTML table.
- Tables are for presenting tabular data, not for design!
3. Form
- Create a web page containing a form where users should input the following data:
- Name (text).
- Age (radio buttons with options "<18", "19-35", "36-48" and ">49").
- Profession (text but with some predefined suggestions — use a datalist).
- Country (a dropdown box – add some countries).
- Interests (a list where users can check several – make up some choices).
- How did the user find out about the site (larger text field).
- The name and country fields should be required.
- The form should also have a submit button, use the button element.
- Each field should have a label.
- Validate the page when you are finished.
- Try to submit the form and verify what happens in the URL bar using POST and GET as the form methods.
What did I learn:
- How to create an HTML form.
- How to use labels to improve accessibility.
- How to use character entities.
- The difference between "GET" and "POST" action in forms (more about this later).
4. Extra
- Pick a webpage from a site you frequently visit.
- Without inspecting its source code, try recreating its structure using proper semantic HTML.
- Validate the HTML code.